Shot Peening
The most important objectives of shot peening are:
- to incease the fatigue strength
- to increase the fatigue life
- to prevent stress corrosion
- to delay stress corrosion fatigue
- to prevent the formation and propagation of cracks
This process is applicable on all metallic parts
Higher fatigue strength allows higher load duration of your parts or higher safety margin.
Your parts will get more durable or the fatigue strength for finite life will be increased.
Examples:
- higher performance by the same weight or less weight by the same performance
- higher performance by the same dimensions or smaller dimensions by the same performance
- higher performance by the same material or greater material selection by the same performance
- higher performance by the same surface finish or lower surface finish by the same performance
The improvement of the fatigue life leads to:
- improving the reputation of the products
- Cost reduction in service and under guarantee
- higher fatigue life of components
- higher safety margins on components
- reinforcing already designed components without changing materials or dimensions
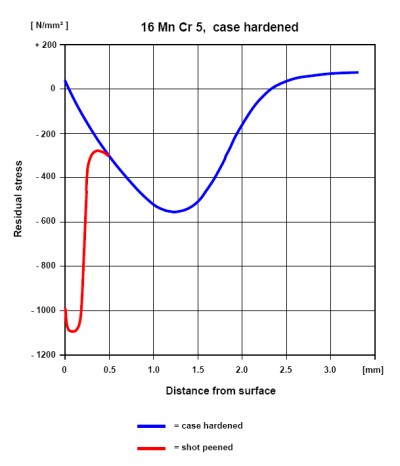
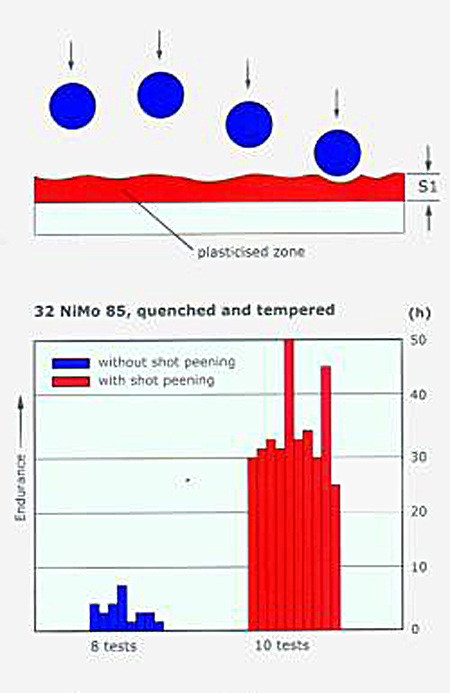
The elastic deformation generates high compressive residual stress in the plastically deformed surface layer.
This surface layer is relieved from applied tensile stress and increases the fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking and corrosion fatigue of the components. High compressive residual stress prevents also the formation and propagation of cracks.
Shot peening is extremely valuable on components with a high stress concentration factor, with high notch sensitivity, with high torsional or bending stress, with percussive load, made of brittle material, hardened material or made of very hard steel. (e.g. valves, springs, percussion pistons, etc.).
Furthermore, the shot peening and blasting process can also be used for compacting, cleaning, stripping, texturing, roughening, matting, smoothening, deburring, skiving, cutting, engraving and to form thin-walled components in the elastically range.
Influence of shot peening
In the shot peening process small spherical particles are propelled by air pressure or a centrifugal acceleration against the surface of a finished part and act like tiny sledge hammers which plastically and elastically deform the material in the surface layer of components. Hertzian Stress deform the material below the surface. Both effects appear simultaneous and are influenced by the shot peening parameters.
